Abstract:
The choroid plexus (ChP) is an extensively vascularized tissue that protrudes into the brain ventricular system of all vertebrates. This highly specialized structure, consisting of the polarized epithelial sheet and underlying stroma, serves a spectrum of functions within the central nervous system (CNS), most notably the production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The epithelial cells of the ChP have the competence to tightly modulate the biomolecule composition of CSF, which acts as a milieu functionally connecting ChP with other brain structures. This review aims to eloquently summarize the current knowledge about the development of ChP. We describe the mechanisms that control its early specification from roof plate followed by the formation of proliferative regions-cortical hem and rhombic lips-feeding later development of ChP. Next, we summarized the current knowledge on the maturation of ChP and mechanisms that control its morphological and cellular diversity. Furthermore, we attempted to review the currently available battery of molecular markers and mouse strains available for the research of ChP, and identified some technological shortcomings that must be overcome to accelerate the ChP research field. Overall, the central principle of this review is to highlight ChP as an intriguing and surprisingly poorly known structure that is vital for the development and function of the whole CNS. We believe that our summary will increase the interest in further studies of ChP that aim to describe the molecular and cellular principles guiding the development and function of this tissue.
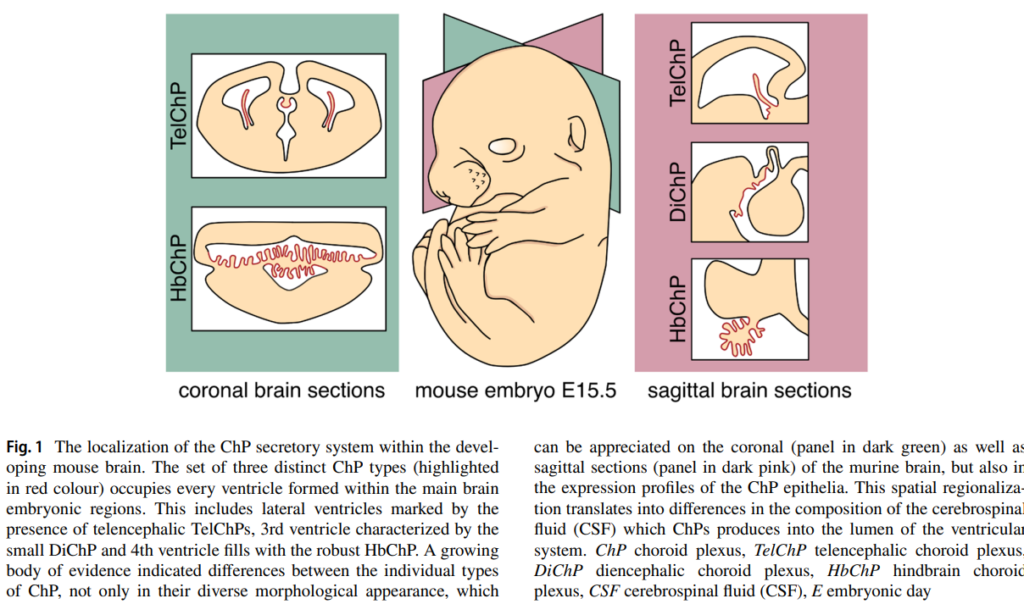
Authors:
Petra Kompaníková 1, Vítězslav Bryja 1 2
Affiliations:
1 Department of Experimental Biology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, 62500, Brno, Czech Republic.
2 Department of Cytokinetics, Institute of Biophysics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, 61265, Brno, Czech Republic.