Van Gogh-like (Vangl) and Prickle (Pk) are core components of the non-canonical Wnt planar cell polarity pathway that controls epithelial polarity and cell migration. Studies in vertebrate model systems have suggested that Vangl and Pk may also inhibit signaling through the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway, but the functional significance of this potential cross-talk is unclear. In the nematode C. elegans, the Q neuroblasts and their descendants migrate in opposite directions along the anteroposterior body axis. The direction of these migrations is specified by Wnt signaling, with activation of canonical Wnt signaling driving posterior migration, and non-canonical Wnt signaling anterior migration. Here, we show that the Vangl ortholog VANG-1 influences the Wnt signaling response of the Q neuroblasts by negatively regulating canonical Wnt signaling. This inhibitory activity depends on a carboxy-terminal PDZ binding motif in VANG-1 and the Dishevelled ortholog MIG-5, but is independent of the Pk ortholog PRKL-1. Moreover, using Vangl1 and Vangl2 double mutant cells, we show that a similar mechanism acts in mammalian cells. We conclude that cross-talk between VANG-1/Vangl and the canonical Wnt pathway is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that ensures robust specification of Wnt signaling responses. Více informací
Similar Posts
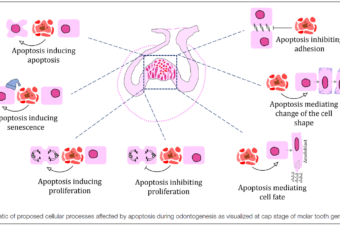
Role of Cell Death in Cellular Processes During Odontogenesis
Abstract: The development of a tooth germ in a precise size, shape, and position in... Read More
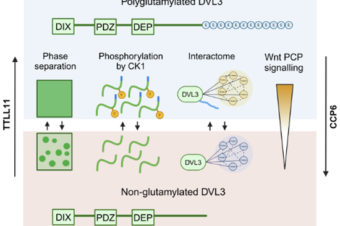
Carboxy-terminal polyglutamylation regulates signalling and phase separation of the Dishevelled protein
Abstract Polyglutamylation is a reversible posttranslational modification that is catalyzed by enzymes of the tubulin... Read More
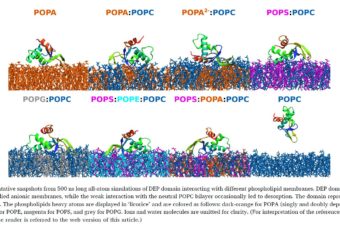
Binding of DEP domain to phospholipid membranes: More than just electrostatics
Abstract: Over the past decades an extensive effort has been made to provide a more... Read More
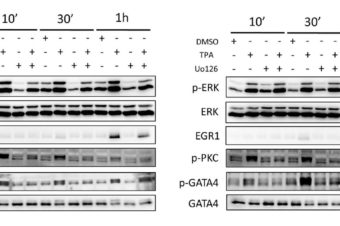
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate increases cardiomyogenesis through PKC/ERK signaling
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is the most widely used diacylglycerol (DAG) mimetic agent and inducer of protein... Read More
Weak radiofrequency fields affect the insect circadian clock
It is known that the circadian clock in Drosophila can be sensitive to static magnetic... Read More
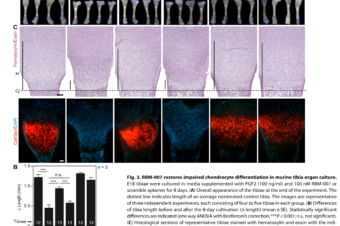
An RNA aptamer restores defective bone growth in FGFR3-related skeletal dysplasia in mice
Abstract: Achondroplasia is the most prevalent genetic form of dwarfism in humans and is caused... Read More