It is known that the circadian clock in Drosophila can be sensitive to static magnetic fields (MFs). Man-made radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields have been shown to have effects on animal orientation responses at remarkably weak intensities in the nanotesla range. Here, we tested if weak broadband RF fields also affect the circadian rhythm of the German cockroach (Blatella
Similar Posts
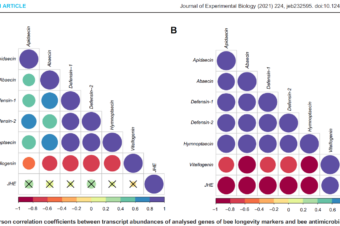
Winter honeybee (Apis mellifera) populations show greater potential to induce immune responses than summer populations after immune stimuli
Abstract: In the temperate climates of central Europe and North America, two distinct honeybee (Apis... Read More
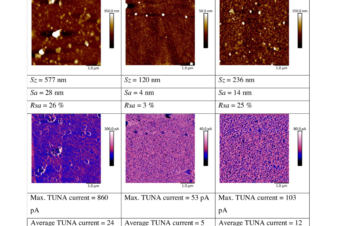
Conducting composite films based on chitosan or sodium hyaluronate. Properties and cytocompatibility with human induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract: Novel composite films combining biocompatible polysaccharides with conducting polyaniline (PANI) were prepared via the... Read More
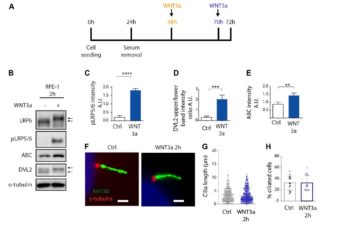
Primary Cilia Formation Does Not Rely on WNT/β-Catenin Signaling
Abstract: Primary cilia act as crucial regulators of embryo development and tissue homeostasis. They are... Read More
Activity of Smurf2 Ubiquitin Ligase Is Regulated by the Wnt Pathway Protein Dishevelled
Cells 2020, 9(5), 1147. ABSTRACT Wnt and BMP signaling pathways are two key molecular machineries... Read More
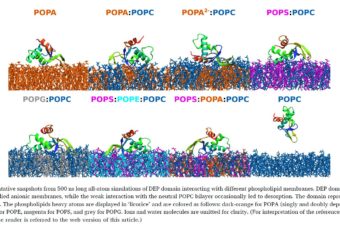
Binding of DEP domain to phospholipid membranes: More than just electrostatics
Abstract: Over the past decades an extensive effort has been made to provide a more... Read More
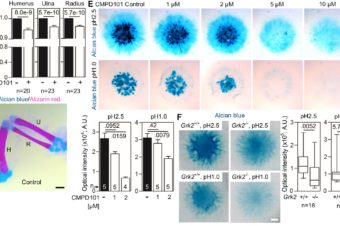
Mutations in GRK2 cause Jeune syndrome by impairing Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling
Mutations in genes affecting primary cilia cause ciliopathies, a diverse group of disorders often affecting... Read More