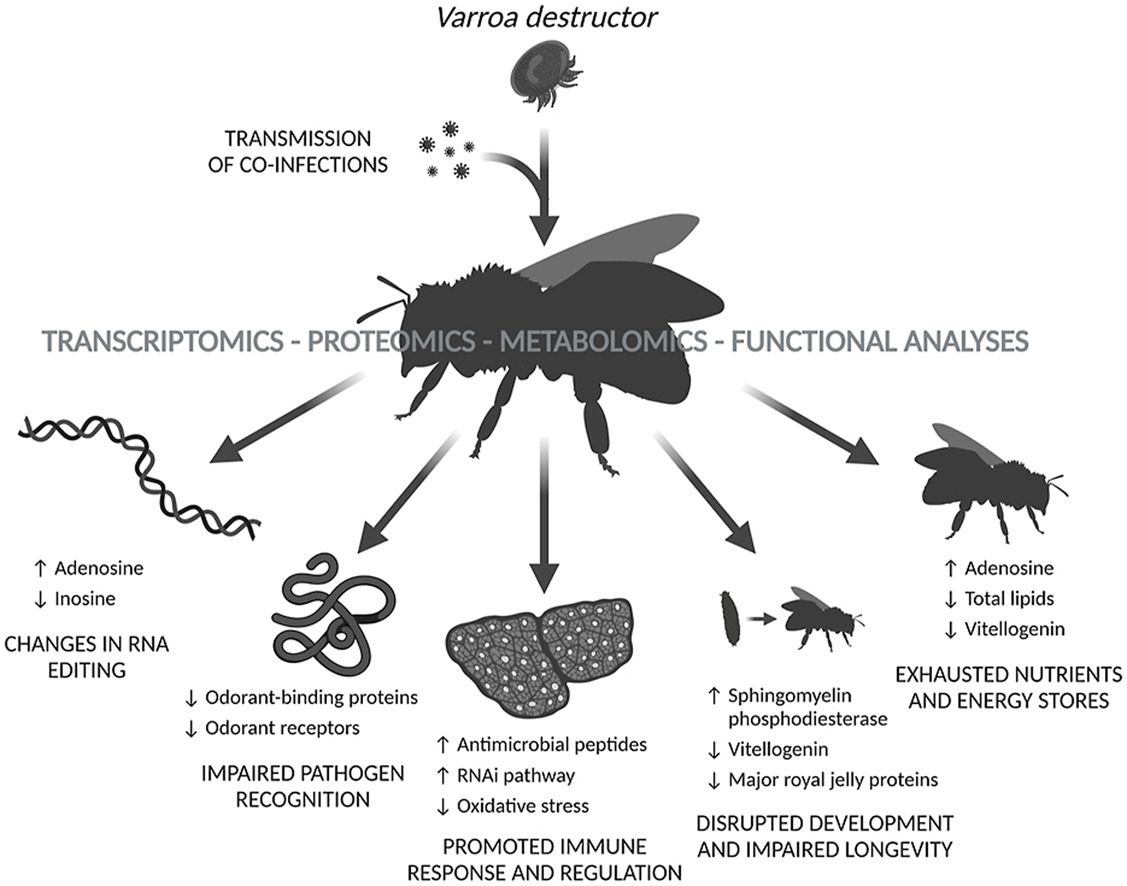
Omics-based analysis of honey bee (Apis mellifera) response to Varroa sp. parasitisation and associated factors reveals changes impairing winter bee generation
AbstractThe extensive annual loss of honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) represents a global problem affecting agriculture and biodiversity. The parasitic mite Varroa destructor, associated with viral co-infections, plays a key role in this loss. Despite years of intensive research, the … Read More
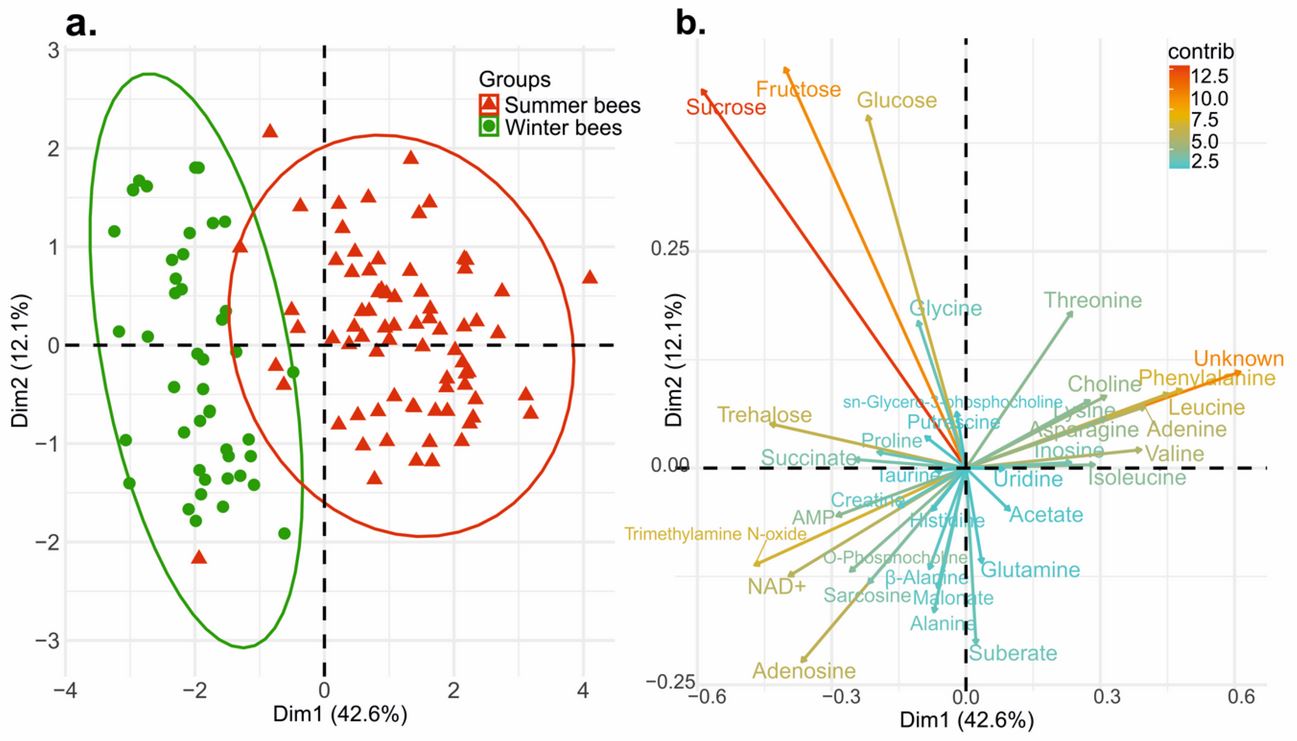
1H NMR Profiling of Honey Bee Bodies Revealed Metabolic Differences between Summer and Winter Bees
Abstract: In temperate climates, honey bee workers of the species Apis mellifera have different lifespans depending on the seasonal phenotype: summer bees (short lifespan) and winter bees (long lifespan). Many studies have revealed the biochemical parameters involved in the lifespan … Read More

Plant-based and immunostimulant-enhanced diets modulate oxidative stress, immune and haematological indices in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of three commercial diets, standard, immunostimulant-supplemented (β-glucan, vitamins C and E) and plant-based, on the degree of oxidative stress in tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Selected immune and … Read More

Atlas of Science
Our article about seasonal changes of honey bee physiological and immune parameters is now listed in Atlas of Science.

Changes in haemolymph parameters and insect ability to respond to immune challenge during overwintering
Abstract: Overwintering is a challenging period in the life of temperate insects. A limited energy budget characteristic of this period can result in reduced investment in immune system. Here, we investigated selected physiological and immunological parameters in laboratory-reared and field-collected … Read More
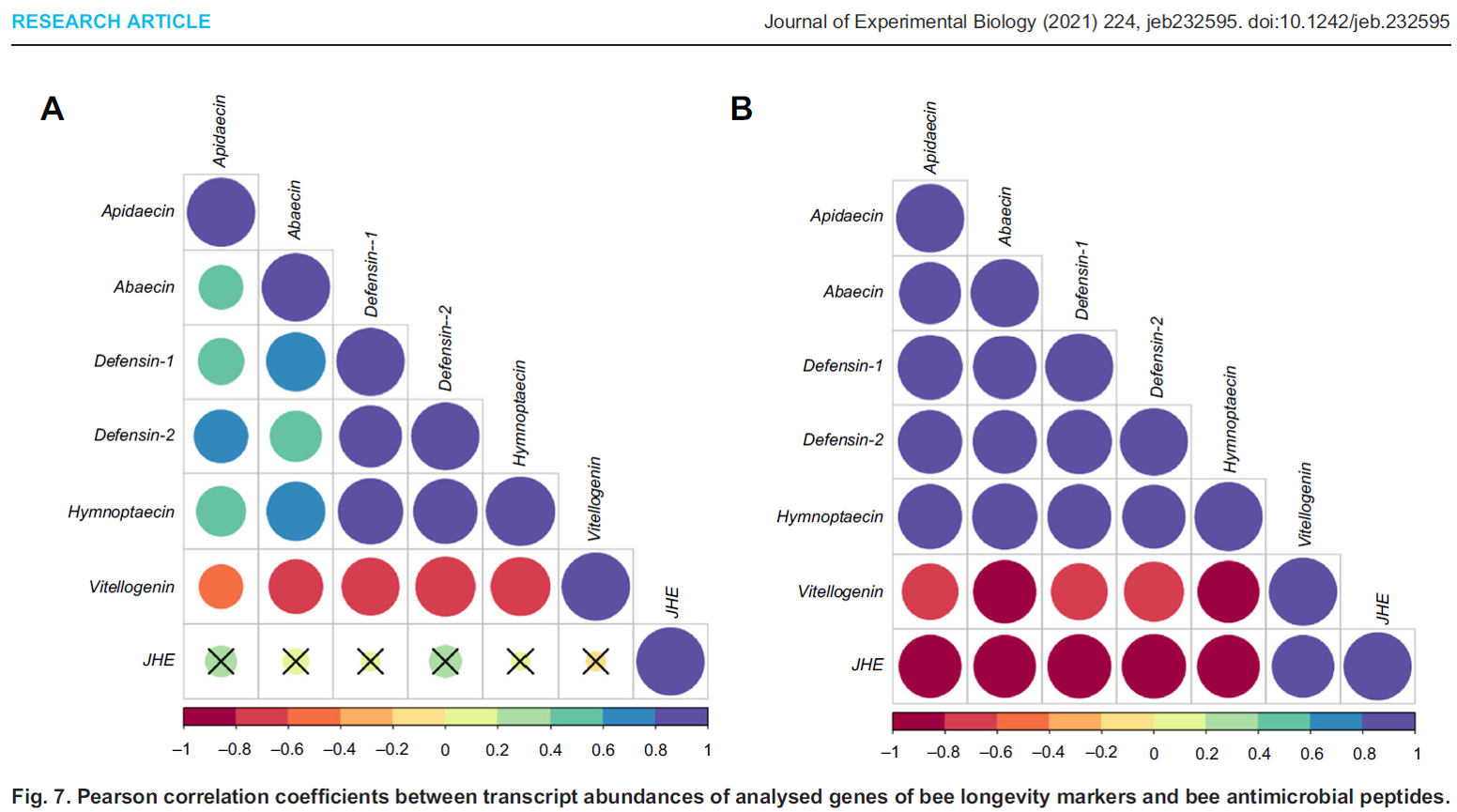
Winter honeybee (Apis mellifera) populations show greater potential to induce immune responses than summer populations after immune stimuli
Abstract: In the temperate climates of central Europe and North America, two distinct honeybee (Apis mellifera) populations are found in colonies: short-living summer bees emerge in spring and survive until summer, whereas long-living winter bees emerge in late August and … Read More
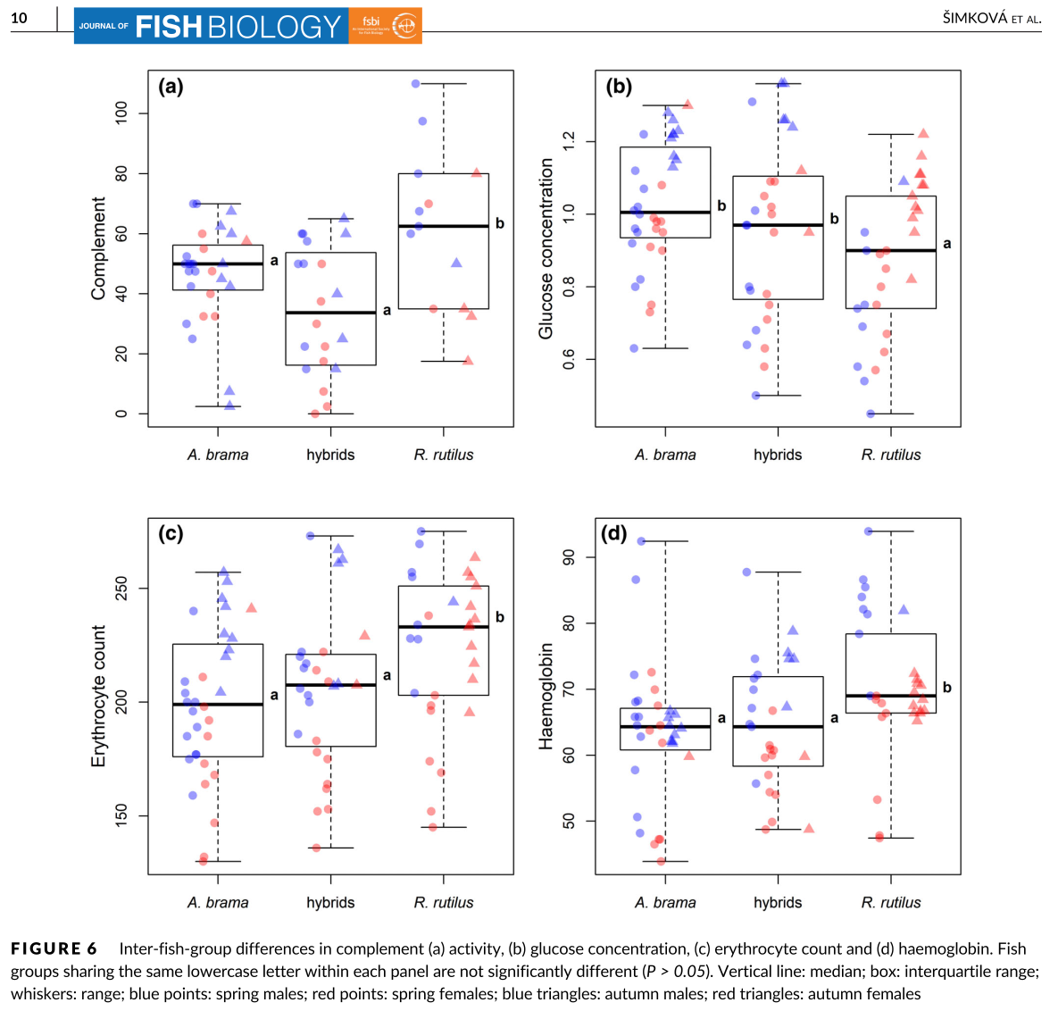
Vigour-related traits and immunity in hybrids of evolutionary divergent cyprinoid species: advantages of hybrid heterosis?
Abstract Hybrid advantage, described as the superiority of hybrids in some traits over their parents and termed the “heterosis effect,” is widely documented in the case of reciprocal crosses of parental species (i.e., hybrids representing the F1 generation). In fish, … Read More
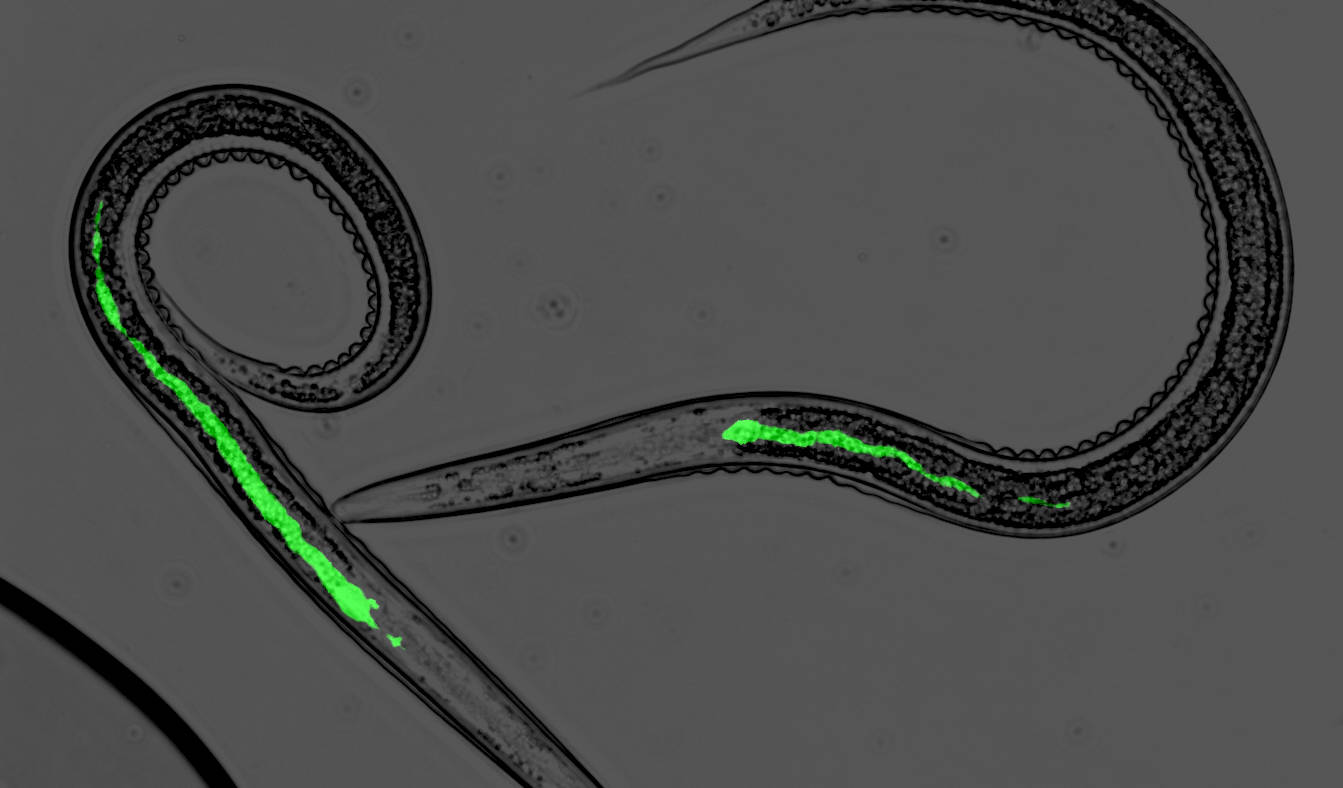
Special Issue „Insects, Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria“
Dear Colleagues, Insect pathogenic nematodes (entomopathogenic nematodes—EPNs) are lethal parasites to their hosts, and are frequently used as biological agents in the control of insect pests. Lethality may be as a result of the virulence factors provided by the nematodes … Read More
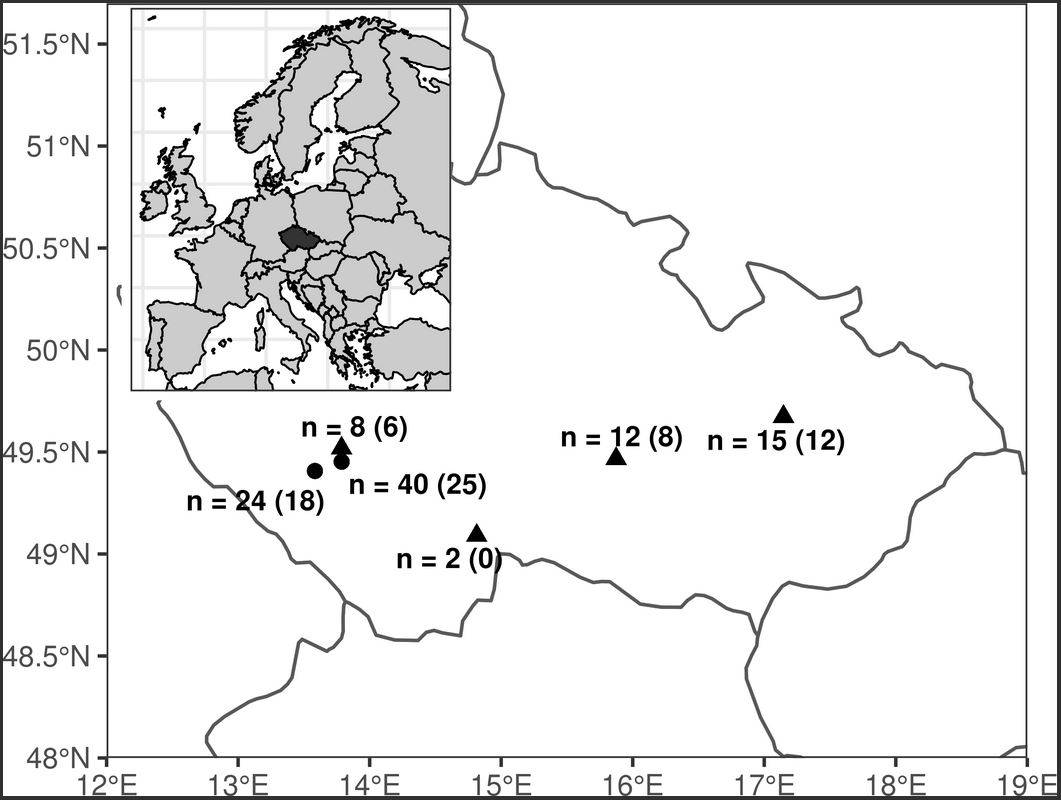
Differences in the growth rate and immune strategies of farmed and wild mallard populations
Individuals reared in captivity are exposed to distinct selection pressures and evolutionary processes causing genetic and phenotypic divergence from wild populations. Consequently, restocking with farmed individuals may represent a considerable risk for the fitness of free-living populations. Supportive breeding on … Read More
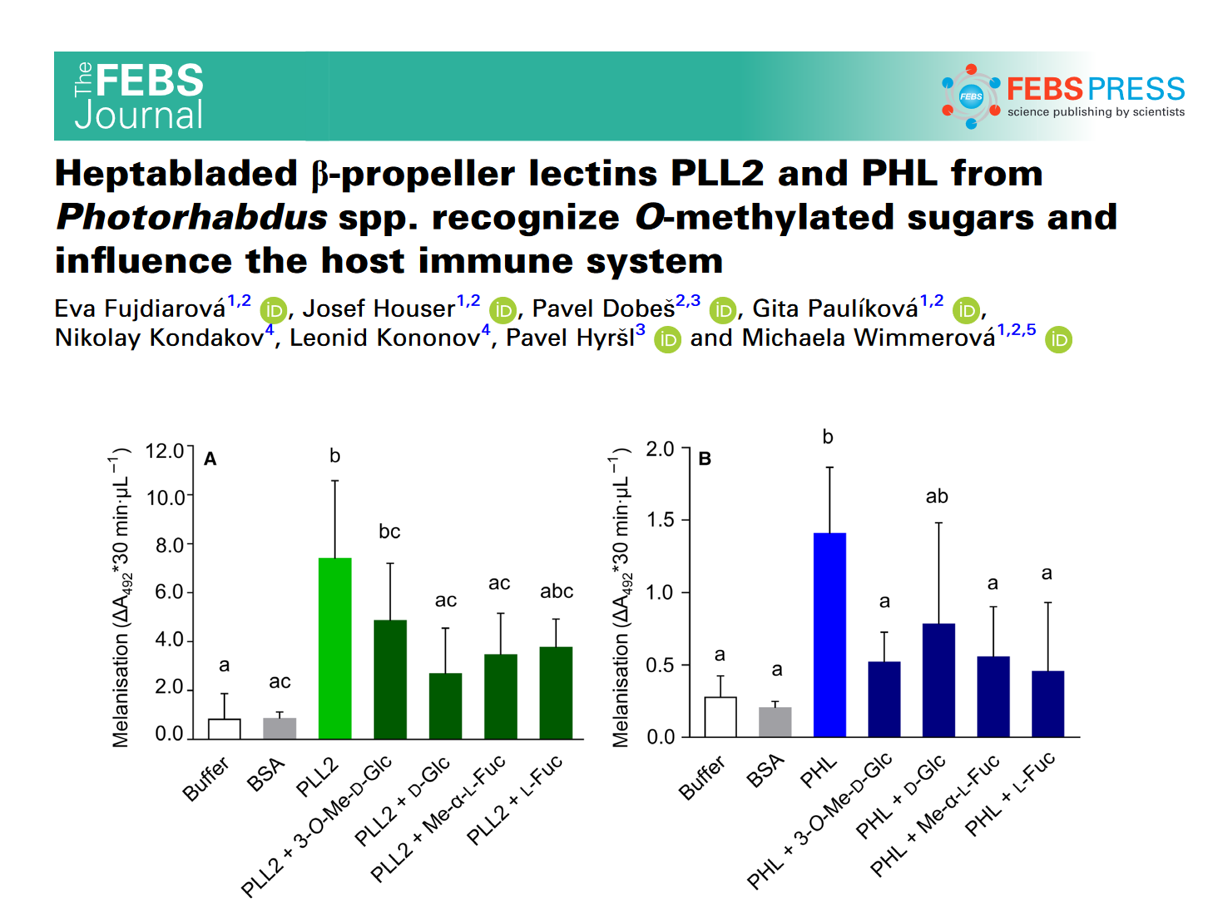
Heptabladed β‐propeller lectins PLL2 and PHL from Photorhabdus spp. recognize O‐methylated sugars and influence the host immune system
O‐methylation is an unusual sugar modification with a function that is not fully understood. Given its occurrence and recognition by lectins involved in the immune response, methylated sugars were proposed to represent a conserved pathogen‐associated molecular pattern. We describe the … Read More

Bioactive Excreted/Secreted Products of Entomopathogenic Nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Inhibit the Phenoloxidase Activity during the Infection
Insects 2020, 11(6), 353; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060353 ABSTRACT: Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) are efficient insect parasites, that are known for their mutualistic relationship with entomopathogenic bacteria and their use in biocontrol. EPNs produce bioactive molecules referred to as excreted/secreted products (ESPs), which have … Read More

Effects of trichothecene mycotoxin T-2 toxin on haematological and immunological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Helena Modra, Miroslava Palikova, Pavel Hyrsl, Jana Bartonkova, Ivana Papezikova, Zdenka Svobodova, Jana Blahova, Jan Mares The aim of this study was to assess the effects of T-2 toxin–contaminated feed (at concentrations of 1.0 and 1.8 mg/kg) on the rainbow … Read More

The Effect of Foraging on Bumble Bees, Bombus terrestris, Reared under Laboratory Conditions
ABSTRACT: Bumble bees are important pollinators broadly used by farmers in greenhouses and under conditions in which honeybee pollination is limited. As such, bumble bees are increasingly being reared for commercial purposes, which brings into question whether individuals reared under … Read More

Changes in physiological and immune parameters of bees during the year – Differences between short-lived and long-lived generations of bees are not only in what activities they do
For beekeepers, it is important to know what proportion of long-lived bees are in the bee population already at the beginning of autumn, because this fact decides whether or not the bee population will survive the winter. Unfortunately, these two … Read More

Conference
We attended the conference International Congress on Invertebrate Pathology and Microbial Control & 52nd Annual Meeting of the Society for Invertebrate Pathology & 17th Meeting of the IOBC‐WPRS Working Group “Microbial and Nematode Control of Invertebrate Pests”.

The Year of the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) with Respect to Its Physiology and Immunity: A Search for Biochemical Markers of Longevity
It has been known for many years that in temperate climates the European honey bee, Apis mellifera, exists in the form of two distinct populations within the year, short-living summer bees and long-living winter bees. However, there is only limited … Read More

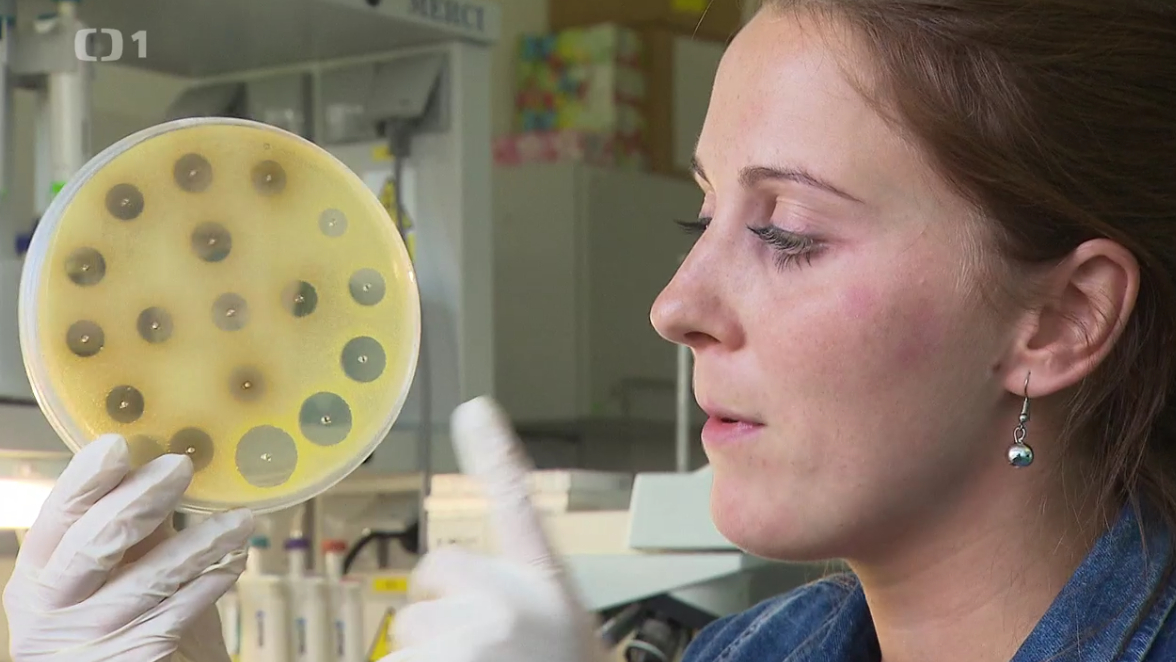
Pavel Hyršl about life of bees in the Czech television!
Pavel Hyršl as an expert on bees and their life gave an interview to the Czech television on occasion of the World Bee Day – 20th May 2019. See the interview here: https://www.ceskatelevize.cz/porady/10435049455-dobre-rano/319291310020047/video/697290,697297,697307
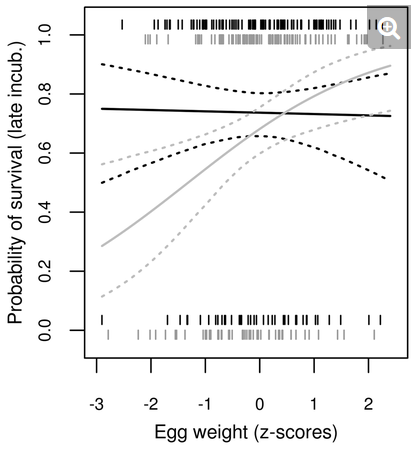
The hidden function of egg white antimicrobials: egg weight-dependent effects of avidin on avian embryo survival and hatchling phenotype
By: Eva Krkavcová, Jakub Kreisinger, Ludmila Hyánková, Pavel Hyršl, Veronika Javůrková Published in: Open Biology ABSTRACT Avidin is a key egg white antimicrobial protein with strong binding capacity for biotin, an essential growth and immune cell precursor. As such, it … Read More

Puncture vs. reflex bleeding: Haemolymph composition reveals significant differences among ladybird species (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), but not between sampling methods
Michal KNAPP1, Pavel DOBEŠ2, Michal ŘEŘICHA1, Pavel HYRŠL2 1 Department of Ecology, Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Prague, Czech Republic; e-mails: knapp@fzp.czu.cz, rericham@fzp.czu.cz 2 Department of Animal Physiology and Immunology, Institute of Experimental Biology, Faculty … Read More

