Congenital heart defects, dysmorphic facial features and intellectual developmental disorders (CHDFIDD) syndrome in humans was recently associated with mutation in CDK13 gene. In order to assess the loss of function of Cdk13 during mouse development, we employed gene trap knock-out (KO) allele in Cdk13 gene. Embryonic lethality of Cdk13-deficient animals was observed by the embryonic day (E) 16.5, while live embryos were observed on E15.5. At this stage, improper development of multiple organs has been documented, partly resembling defects observed in patients with mutated CDK13. In particular, overall developmental delay, incomplete secondary palate formation with variability in severity among Cdk13-deficient animals or complete midline deficiency, kidney failure accompanied by congenital heart defects were detected. Based on further analyses, the lethality at this stage is a result of heart failure most likely due to multiple heart defects followed by insufficient blood circulation resulting in multiple organs dysfunctions. Thus, Cdk13 KO mice might be a very useful model for further studies focused on delineating signaling circuits and molecular mechanisms underlying CHDFIDD caused by mutation in CDK13 gene.
Similar Posts
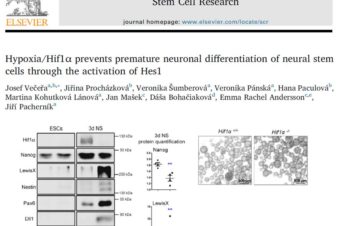
Hypoxia/Hif1α Prevents Premature Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells Through the Activation of Hes1
Stem Cell Res. 2020 May;45:101770 ABSTRACT: Embryonic neural stem cells (NSCs), comprising neuroepithelial and radial... Read More
Invertebrate Magnetoreception – In Between Orientation and General Sensitivity
Elsevier Collection of Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809324-5.24159-X ABSTRACT: The discovery of magnetic sensitivity in... Read More
Variability in the Clearance of Lead Oxide Nanoparticles Is Associated with Alteration of Specific Membrane Transporters
Lead oxide nanoparticles (PbONPs), upon their entry into the lungs via inhalation, induce structural changes... Read More
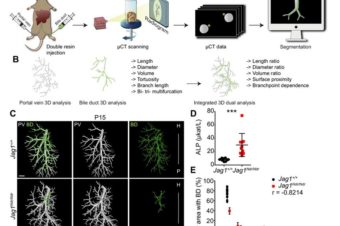
DUCT reveals architectural mechanisms contributing to bile duct recovery in a mouse model for Alagille syndrome
Abstract: Organ function depends on tissues adopting the correct architecture. However, insights into organ architecture... Read More
The effects of nano-sized PbO on biomarkers of membrane disruption and DNA damage in a sub-chronic inhalation study on mice
Although the production of engineered nanoparticles increases our knowledge of toxicity and mechanisms of bioactivity... Read More
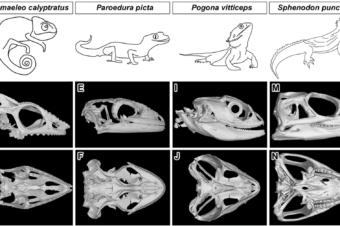
Coordinated labio-lingual asymmetries in dental and bone development create a symmetrical acrodont dentition
Abstract Organs throughout the body develop both asymmetrically and symmetrically. Here, we assess how symmetrical... Read More