Abstract:
Achondroplasia is the most prevalent genetic form of dwarfism in humans and is caused by activating mutations in FGFR3 tyrosine kinase. The clinical need for a safe and effective inhibitor of FGFR3 is unmet, leaving achondroplasia currently incurable.
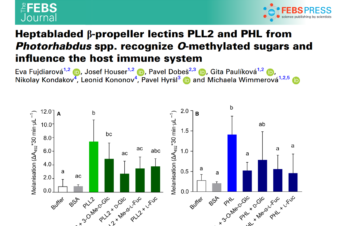
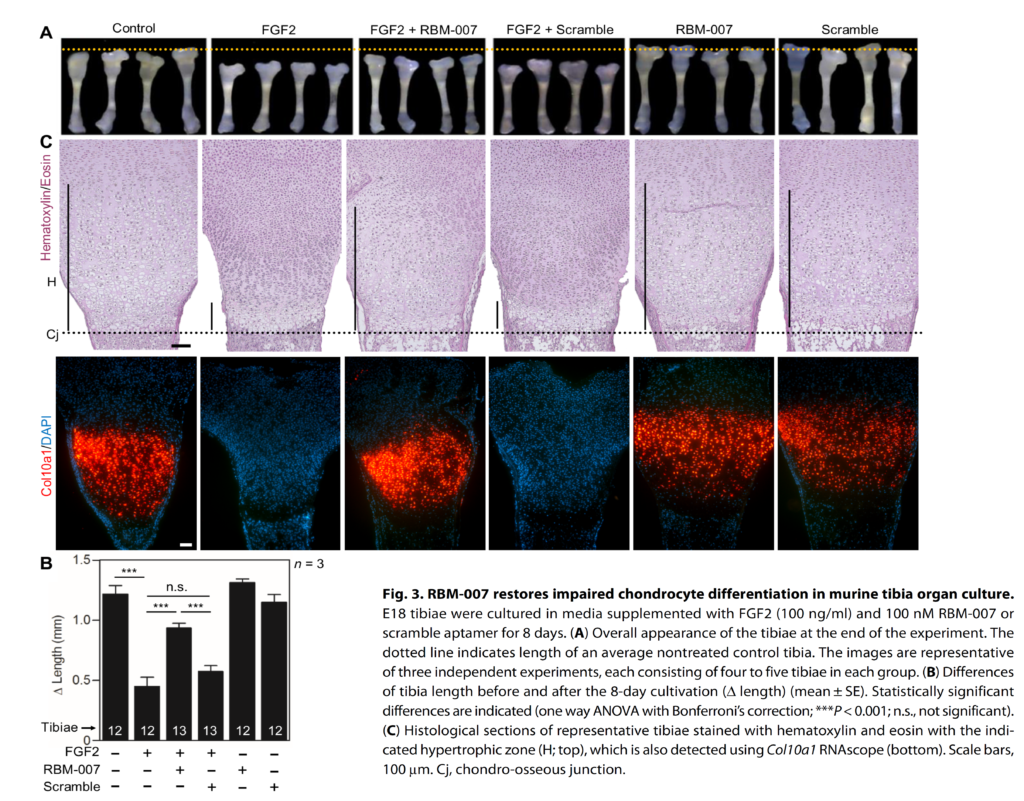
Here, we evaluated RBM-007, an RNA aptamer previously developed to neutralize the FGFR3 ligand FGF2, for its activity against FGFR3. In cultured rat chondrocytes or mouse embryonal tibia organ culture, RBM-007 rescued the proliferation arrest, degradation of cartilaginous extracellular matrix, premature senescence, and impaired hypertrophic differentiation induced by FGFR3 signaling. In cartilage xenografts derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from individuals with achondroplasia, RBM-007 rescued impaired chondrocyte differentiation and maturation. When delivered by subcutaneous injection, RBM-007 restored defective skeletal growth in a mouse model of achondroplasia.
We thus demonstrate a ligand-trap concept of targeting the cartilage FGFR3 and delineate a potential therapeutic approach for achondroplasia and other FGFR3-related skeletal dysplasias.
Takeshi Kimura 1; Michaela Bosakova 2,3,4; Yosuke Nonaka 5; Eva Hruba 4; Kie Yasuda 1; Satoshi Futakawa 5; Takuo Kubota 1; Bohumil Fafilek 2,3,4; Tomas Gregor 2,3; Sara Abraham 2; Regina Gomolkova 2,4; Silvie Belaskova 3; Martin Pesl 2,3,6; Fabiana Csukasi 7,8; Ivan Duran 7,8; Masatoshi Fujiwara 5; Michaela Kavkova 9; Tomas Zikmund 9; Josef Kaiser 9; Marcela Buchtova 4,10; Deborah Krakow 7; Yoshikazu Nakamura 11,12; Keiichi Ozono 13; Pavel Krejci 14,3,4
1 Department of Pediatrics, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, 565-0871 Osaka, Japan.
2 Department of Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University, 62500 Brno, Czech Republic.
3 International Clinical Research Center, St. Anne’s University Hospital, 65691 Brno, Czech Republic.
4 Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics, Czech Academy of Sciences, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic.
5 RIBOMIC Inc., Tokyo 108-0071, Japan.
6 First Department of Internal Medicine-Cardioangiology, St. Anne’s University Hospital, Masaryk University, 65691 Brno, Czech Republic.
7 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA.
8 Networking Research Center on Bioengineering, Biomaterials, and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN)-LABRET, University of Málaga, IBIMA-BIONAND, 29071 Málaga, Spain.
9 Central European Institute of Technology, Brno University of Technology, 61200 Brno, Czech Republic.
10 Department of Experimental Biology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, 62500 Brno, Czech Republic.
11 RIBOMIC Inc., Tokyo 108-0071, Japan.
12 Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 108-8639, Japan.
13 Department of Pediatrics, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, 565-0871 Osaka, Japan.
14 Department of Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University, 62500 Brno, Czech Republic.