Objectives:
The aim of this study is to evaluate the seroprevalence of antibodies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (Bbsl) and Leptospira interrogans sensu lato (Lisl) and their possible concurrence in domestic cats living in variable conditions in South Moravia in the district of Brno and its environs. Additional objectives were to discover possible differences in seroprevalence between groups of cats living in different living conditions, and to determine the spectrum of Leptospira serogroups in cats in the same places.
Material and methods:
A total of 360 blood sera from domestic cats of 3 different sets were collected during the period 2013–2015. All samples were examined using ELISA for the detection of IgM and IgG antibodies against Bbsl, and the microscopic agglutination test (MAT) for the detection of antibodies against 8 serogroups of Lisl.
Results:
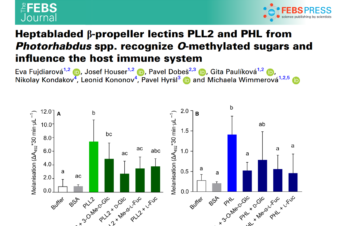
The ELISA method determined 15.8%, 4.8% and 10.3% IgM anti-Borrelia antibodies in the patient group, shelter cats and street cats, respectively. IgG anti-Borrelia antibodies were found in 6.2%, 9.5%, 5.2%, respectively. Antibodies specific for 5 Leptospira serogroups were detected by the use of MAT in 8.8%, 9.5% and 10.3% of cats from the investigated groups. The total positivity of all examined cats for anti-Borrelia antibodies was 18.0% and for anti-Leptospira – 9.2%.
Conclusions:
Cats can be infected with both Bbsl and Lisl. The obtained results are exclusive to the city of Brno and its environs, and are comparable to the limited previous studies. There is a need for further studies of clinical signs of both infections and the possible transmission of Leptospira by ticks.