It is known that the circadian clock in Drosophila can be sensitive to static magnetic fields (MFs). Man-made radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields have been shown to have effects on animal orientation responses at remarkably weak intensities in the nanotesla range. Here, we tested if weak broadband RF fields also affect the circadian rhythm of the German cockroach (Blatella
Similar Posts
Plant-based and immunostimulant-enhanced diets modulate oxidative stress, immune and haematological indices in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of three commercial diets,... Read More
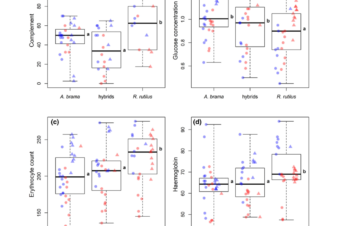
Vigour-related traits and immunity in hybrids of evolutionary divergent cyprinoid species: advantages of hybrid heterosis?
Abstract Hybrid advantage, described as the superiority of hybrids in some traits over their parents... Read More
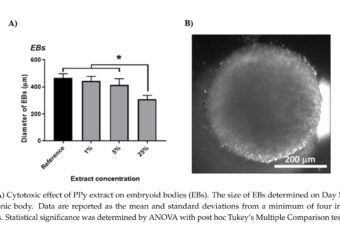
Modulation of Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells by Polypyrrole: The Impact on Neurogenesis
Abstract: The active role of biomaterials in the regeneration of tissues and their ability to... Read More
Changes in haemolymph parameters and insect ability to respond to immune challenge during overwintering
Abstract: Overwintering is a challenging period in the life of temperate insects. A limited energy... Read More
Puncture vs. reflex bleeding: Haemolymph composition reveals significant differences among ladybird species (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), but not between sampling methods
Michal KNAPP1, Pavel DOBEŠ2, Michal ŘEŘICHA1, Pavel HYRŠL2 1 Department of Ecology, Faculty of Environmental... Read More
The Effect of Foraging on Bumble Bees, Bombus terrestris, Reared under Laboratory Conditions
ABSTRACT: Bumble bees are important pollinators broadly used by farmers in greenhouses and under conditions... Read More